General Mobile Radio Service (GMRS) is a licensed two-way radio service in the United States that operates on UHF frequencies. GMRS radios are widely used by families, businesses, and outdoor groups because they provide reliable short-to-medium range communication. However, terrain and obstacles often limit coverage. This is where GMRS repeaters become essential. A GMRS repeater receives a signal on one frequency and retransmits it on another, significantly extending the communication range, often up to 20–30 miles or more depending on location and power.
GMRS Repeater Frequencies List
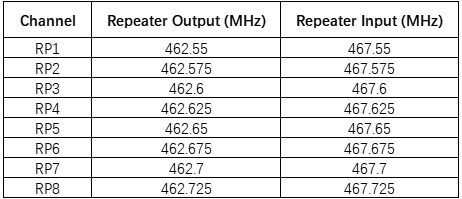
The FCC designates specific GMRS repeater frequencies within the 462 MHz and 467 MHz bands. Repeaters receive on the 467 MHz input frequencies and transmit on the corresponding 462 MHz output frequencies, with a standard 5 MHz offset.
Output (Repeater Transmit): The frequency your radio receives (462.xxx MHz).
Input (Repeater Receive): The frequency your radio transmits (467.xxx MHz).
Here are the eight main GMRS repeater channels:
These GMRS repeater frequencies are standardized, making it easier for licensed users to connect with existing repeaters in their area.
How to Use GMRS Repeater Frequencies
To access GMRS repeater channels, you need a GMRS radio that is repeater capable. Many handheld and mobile GMRS radios come with repeater capability built-in. If you don’t know, ask the walkie talkie manufacturer/seller. Here are the steps to get started:
Step 1: Ensure You Have a GMRS License
The FCC requires a GMRS license, which covers your entire family. The cost is $35 and valid for 10 years. Operating on GMRS repeater frequencies without a license is prohibited.
Step 2: Program the Repeater Channels
Most GMRS radios allow manual or software programming. Enter the repeater output frequency (462 MHz) and input frequency (467 MHz) along with the correct CTCSS/DCS tones provided by the repeater operator.
Step 3: Test and Communicate
Once programmed, your GMRS radio will transmit on the input frequency and receive on the output frequency, allowing you to communicate over much longer distances than simplex operation.
Benefits of GMRS Repeater Frequencies
- Extended Range: Reach 20–30 miles or more, depending on repeater location and output power.
- Reliable Communication: has strong penetration. Overcome obstacles like hills, forests, and buildings.
- Community Networks: Many areas have local repeater groups that support public communication and emergency preparedness.
- Versatility: Useful for off-road groups, emergency responders, businesses, and families.
Conclusion
Understanding and using GMRS repeater frequencies is the key to unlocking the full potential of GMRS radios. By connecting to repeaters, users gain access to extended coverage, better clarity, and reliable communication in both urban and remote environments. Whether you are new to GMRS or an experienced operator, knowing how to program and use repeater channels ensures you stay connected when it matters most.